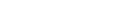Overtime and wage regulations can protect workers who would otherwise be required to work more than they would like at the current rate. Most national countries have overtime laws that may take into account aspects other than humanitarian, such as preserving the health of workers so that they continue to be productive or increase the overall level of employment in the economy.
These laws regulate how to compensate employees for working in excess of a standard workweek.
With certain exceptions related to industry, federal and state law requires that nonexempt employees be paid when they work overtime.
USA
The Fair Labor Standards Act of 1938 (FLSA) introduced two forms of federal wage regulation into the U.S. labor market: a minimum wage and a requirement that an overtime wage at least one and one-half times the straight-time hourly wage.
The law does not limit the number of hours that employees over the age of 16 can work during any workweek. The law does not require the payment of overtime for work on Saturdays, Sundays, holidays, or regular days off unless overtime is worked on those days.
The Fair Labor Standards Act states that any work over 40 hours in a 168-hour period counts as overtime because the average U.S. workweek is 40 hours – that’s eight hours a day five days a week.
The Act applies on a workweek basis. The working week is fixed and the period of 168 hours is regularly repeated – seven consecutive periods of 24 hours.
It doesn’t have to coincide with a calendar week, but it can start any day and at any time of the day. Different workweeks may be established for different employees.
Overtime rate:
Most waged employees must be paid at a wage rate of 150% of their regular hourly rate for hours that exceed 40 in a week.

United Kingdom
Regulations say most workers cannot be forced to work longer than an average of 48 hours a week, but can agree to work longer.
Overtime rate:
The United Kingdom has no minimum statutory levels of overtime pay, and employers are not forced to pay workers for doing overtime. However, the average wage for the total hours worked must not fall below the National Minimum Wage. Employee employment contracts should include details of overtime pay rates and how they’ve worked out.

EU
The European working time directive (EWTD, passed in November 2003) regulates labor and working hours. According to the EWTD, employers must ensure that employees do not work longer than 48 hours, including overtime, during a seven-day period, calculated as an average over a four-month period.
Each worker is entitled to 11 hours of uninterrupted rest per day and 24 hours of uninterrupted rest after each seven-day period, which must be taken within 14 days. Employers must have a time tracking system not only to keep track of overtime hours but also to ensure that employees get their mandatory rest periods.
France
According to French law, the employer is free to require each employee to work overtime up to an annual limit agreed in the applicable collective agreement or, in the absence of a collective agreement, up to a legal limit of 220 hours per year per employee.
Provided that the employer does not require the employee to work outside the legal limits, the employee has no right to refuse to work overtime.
Over this threshold, employees are entitled to “mandatory rest” in addition to financial compensation.
Overtime rate:
Any hour performed over the weekly working time of 35 will be paid at an additional 25% premium on top of your normal rate of pay.
Overtime beyond those hours receives an additional 50% premium.

Spain
Full-time work in Spain is based on a maximum of 40 hours per week, calculated on an annual basis. Overtime at night is illegal, with very few exceptions.
The employer can compensate you for overtime work with paid vacation time.
Overtime rate:
Overtime hours are usually paid at 75% of the basic hourly rate.

Poland
In Poland every hour work more than 8 hours a day and 40 hours a week count as overtime. According to the Polish Labor Law, you are allowed to work a maximum of 150 hours’ overtime per year.
Overtime requires the payment of 100% compensation in addition to the regular remuneration for:
- On Sundays and holidays which are days off according to the employee’s schedule
- Working overtime at night
- A working day that is assigned to an employee in exchange for work on a Sunday or a holiday according to the employee’s schedule.
Overtime rate:
After working 8 hours a day, you are entitled to 50% extra of the standard wage for every hour you work overtime.

Italy
According to Italian law, work performed in excess of 40 hours a week is overtime. Unless otherwise specified, overtime cannot exceed 250 hours per year.
Failure by the employer to comply with these restrictions may result in the collection of administrative penalties.
Overtime rate:
Overtime is usually compensated by an increased rate of pay, ranging from 15 percent to 50 percent depending on the collective agreement and when the overtime takes place.

Sweden
Working Hours Act in Sweden, define a standard working week of 40 hours but also place caps on overtime. No employee can work more than 50 hours of overtime in a calendar month or more than 200 in a calendar year.
Overtime rate:
Overtime is usually rewarded with an additional 50-100% of salary above the standard employee rate.

Germany
Overtime must comply with the maximum working hours – no more than 60 hours per week, on average up to 48 hours over a period of 6 months.
Overtime will usually be compensated instead of free time, although some companies will pay for all overtime hours.
Overtime rate:
Right for compensation for hours worked overtime will be specified in your employment contract.
Some companies claim that a little overtime is a normal part of the job and will not provide additional compensation.

Hungary
According to Labour Law in Hungary, the maximum limit on overtime is 250 hours per calendar year. This can be increased to 300 hours if provided for in the collective agreement. The maximum daily working time is 12, and the weekly working time is 48, including overtime work, so the employee can work a maximum work 4 hours a day overtime and 8 hours overtime a week.
The employer and the employee may agree that the employee voluntarily undertakes 150 hours of additional overtime work on an annual basis.
Overtime rate:
Employees are entitled to a 50 percent wage allowance for overtime work performed in excess of the daily working time (100%, if the work is performed on a rest day).
The agreement between the parties may stipulate the provision of time off in lieu of a wage allowance

Iceland
According to Icelandic Labour Law, employees in this country have to devote a standard time of 40-hours per week to work. Overtime work is limited to 48-hours per week.
Overtime pay is paid for work in excess of 8 hours per day and 40 hours per week.
Overtime rate:
The overtime pay rate per hour in Iceland is 1.0385% of monthly salary per hour of overtime worked.
Employees receiving salaries usually take additional time off work instead of receiving overtime pay.

Serbia
Accoring to an Employment Act, the overtime cannot last longer than eight hours a week. An employee cannot work more than 12 hours a day, including overtime.
Overtime rate:
Overtime is paid at 126% of a regular salary.

Russia
Overtime work must not exceed four hours for two days in a row and 120 hours a year. At the request of the employee, overtime work can be compensated by additional free time instead of an increased salary.
Overtime rate:
Overtime should be compensated in the amount of 150% of the regular hourly rate for the first 2 hours of overtime and 200% of the regular hourly rate for each subsequent hour.

Australia
Generally, a full-time employee may work a maximum of 38 hours per week, unless the employer requires them to work reasonably more hours.
These additional hours will usually be paid as overtime, but there may be variations depending on the nature of the job and the current remuneration, which may determine the maximum normal working hours an employee can work daily or weekly.
Overtime rate:
From Monday to Saturday, overtime work is paid at a rate that is one and a half times higher than the usual salary of employees for the first three hours of overtime work on any day and at twice the usual salary rate for all overtime work he worked after.
At 150% of the employee’s regular working hours for the first two or three hours of overtime.
At 200% of normal working hours per hour after two or three hours of overtime.

India
According to the Factory Act of 1948, every adult (a person who has reached the age of 18) cannot work longer than 48 hours a week and a maximum of 9 hours a day.
Overtime work should be voluntary, not forced by agreement.
Employees should decide whether they want to work overtime or not.
Overtime rate:
Overtime workers will be paid overtime wages at a rate of twice the ordinary rate of wages.

Start managing your time
FREE 14-day trial – no credit card required